FOOD COLORING & APPLICATION


There are two main types of colors:
Natural and Synthetic
Natural and Synthetic
1) Natural Colours.
Natural Colours are extracted from natural matter such as plants, trees and insects. The disadvantage of Natural Colours is that they are:
a) More expensive.
b) Less stable.
c) Weaker
2) Synthetic Colours.
Synthetic colours are manufactured by the ton in batch lots, the most common of which is the AZO DYE (-N=N-). There are hundreds of AZO DYES, which can produce virtually every colour required. Only a handful of these colours have FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approval. The basic colours are two shades of Red, two shades of Blue, a Yellow and an Orange. Other FDA colours are available, but with these basic colours in varying strengths and combinations, virtually every colour can be formulated.
Primary & Lake colours
- There are two types of Food Colours: Primary and Lake
1) Primary Colours. .
Primary Colours are water-soluble and usually used for wet applications.
2) Lake Colours.
Lake Colours impart their colour by dispersion. Lake Colours are manufactured by adsorbing the Primary colour on to Aluminium Hydroxide. This is then dried and very finely milled. Lakes are generally used in Dry Applications where finely divided particles of lake, form a coating on the surface of the product.
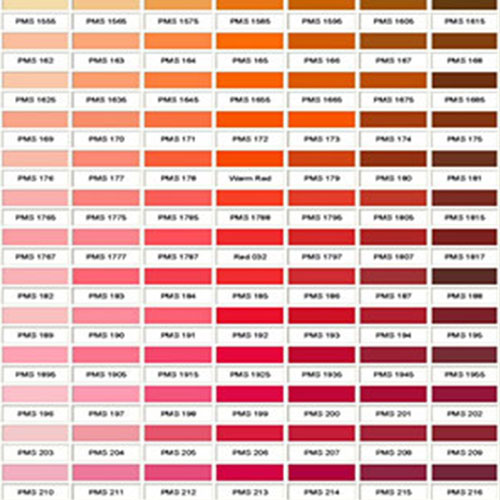
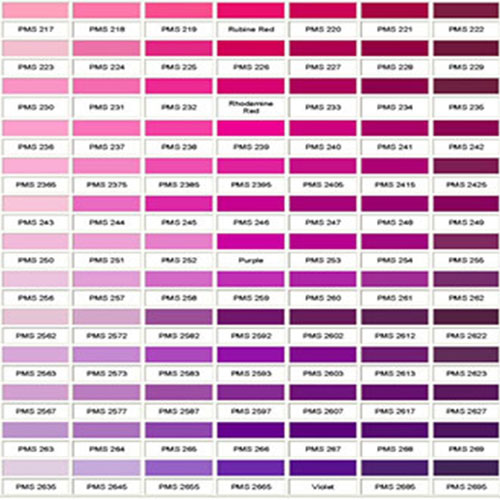
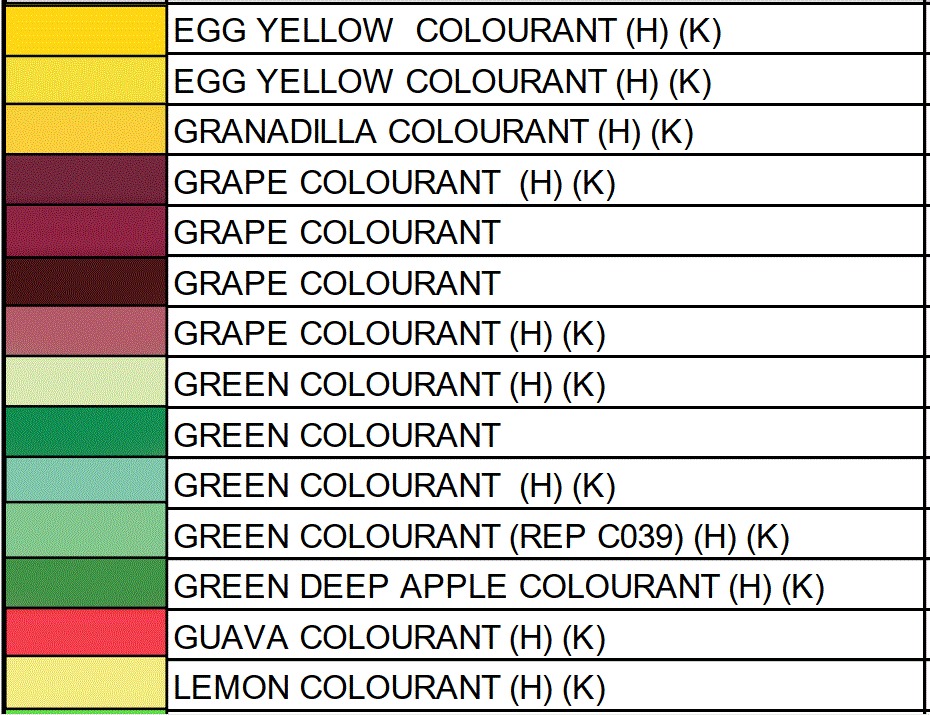
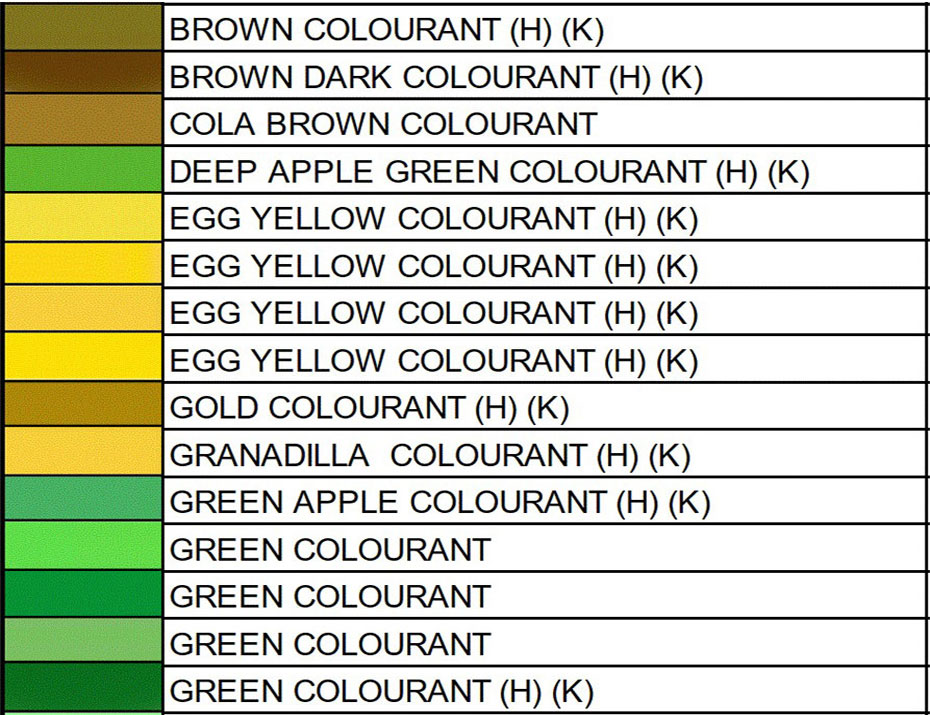
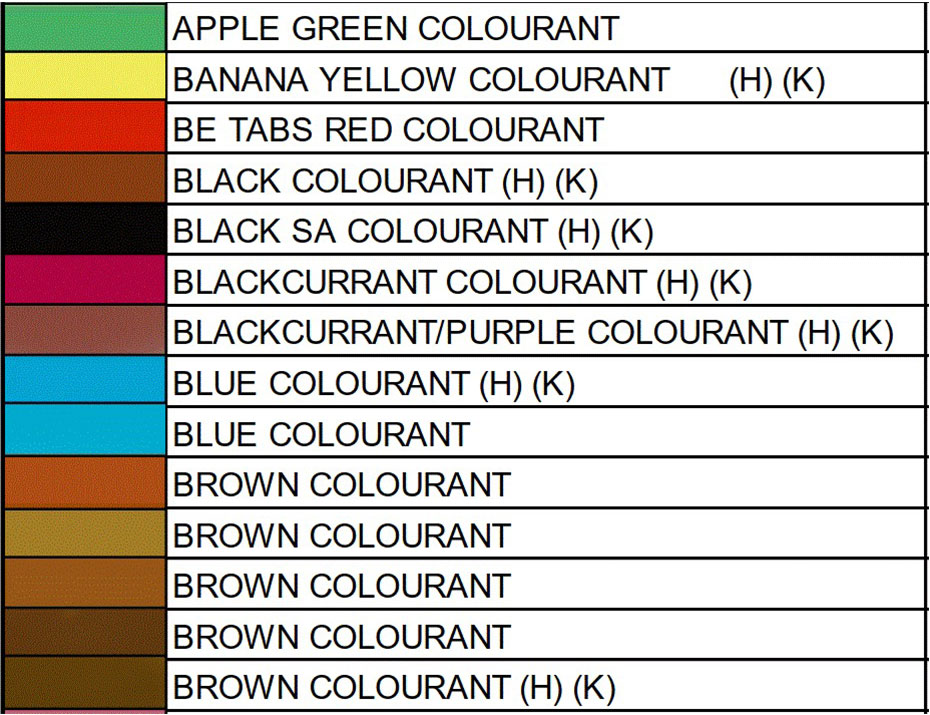
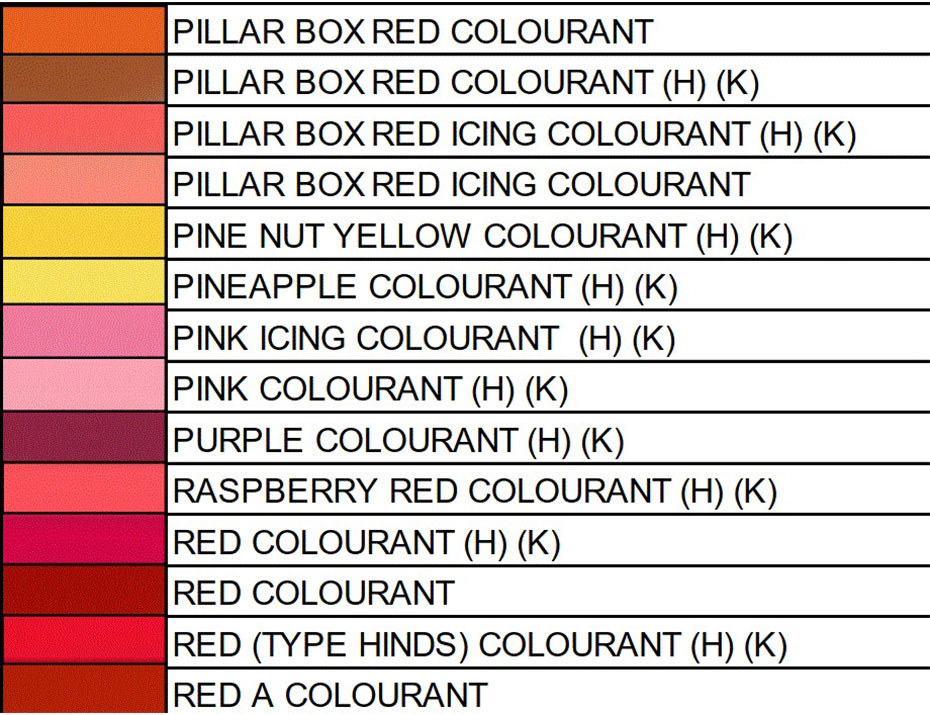
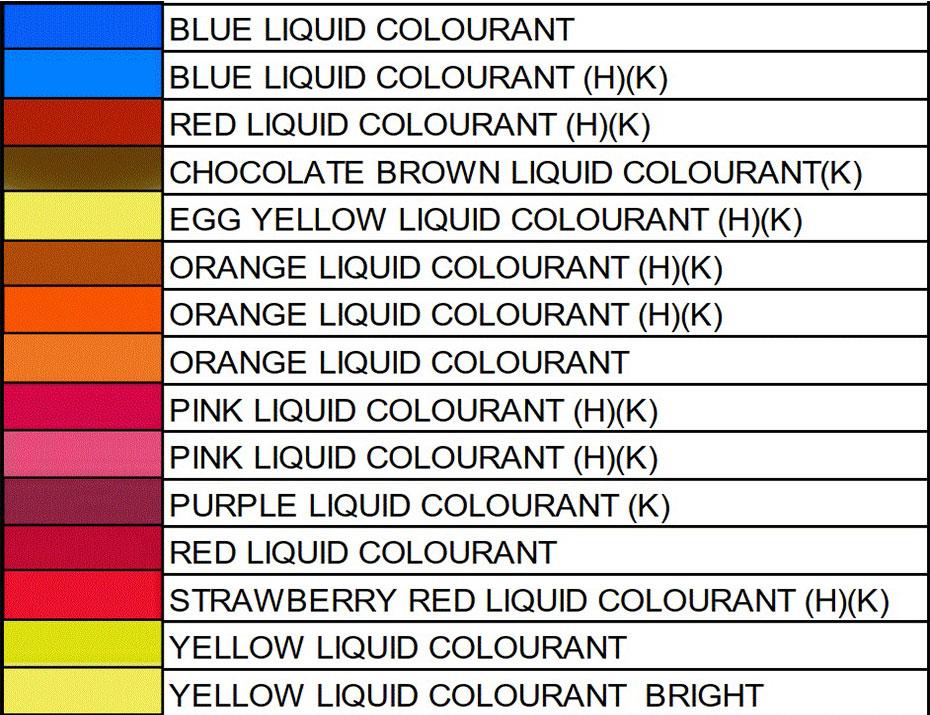
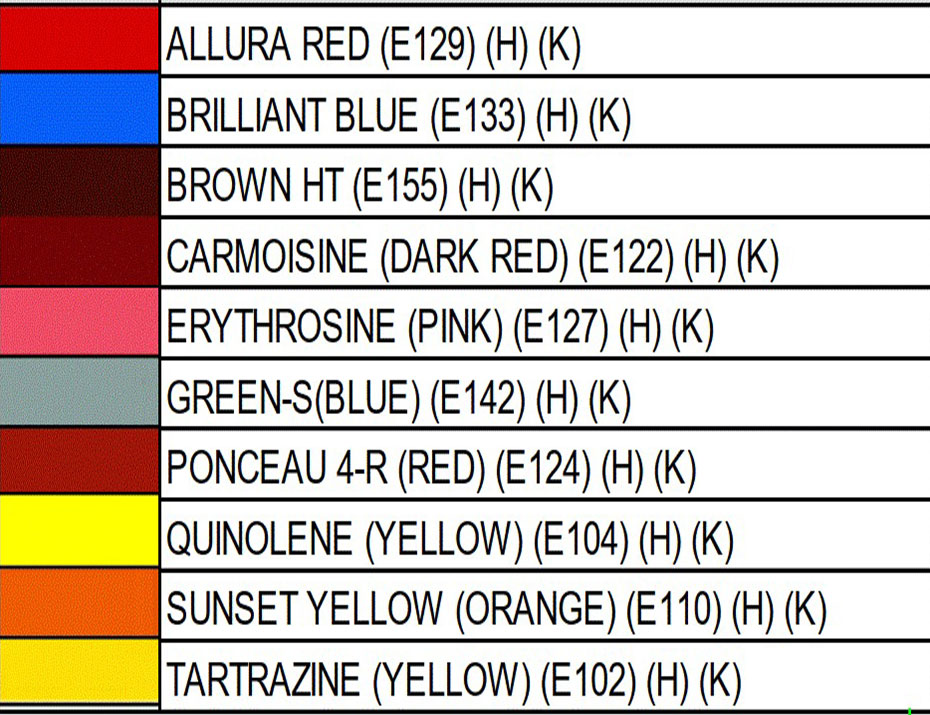
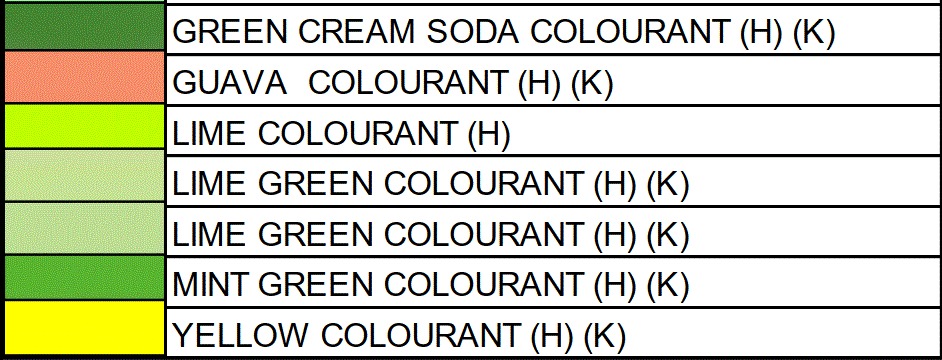
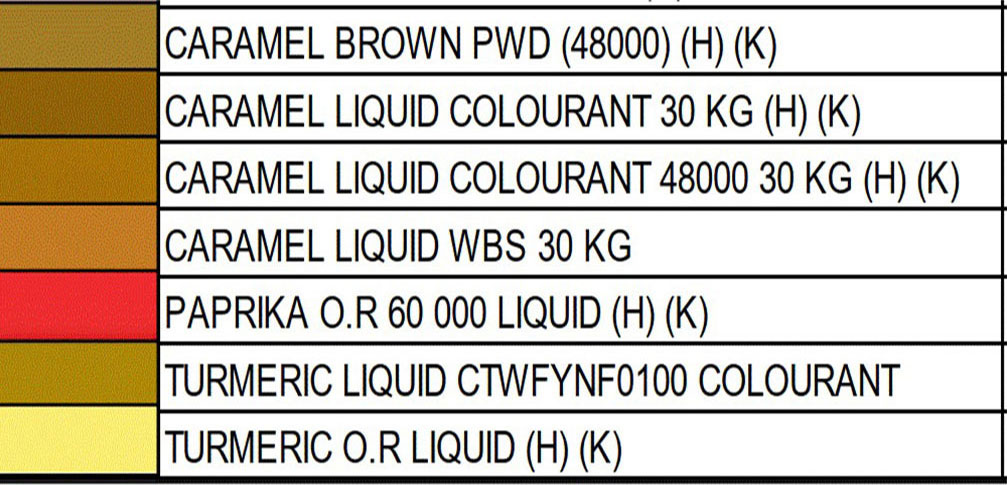
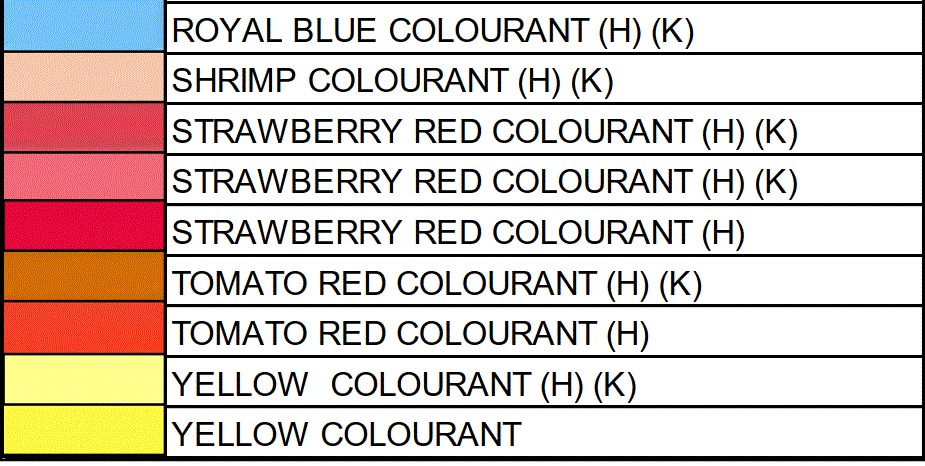
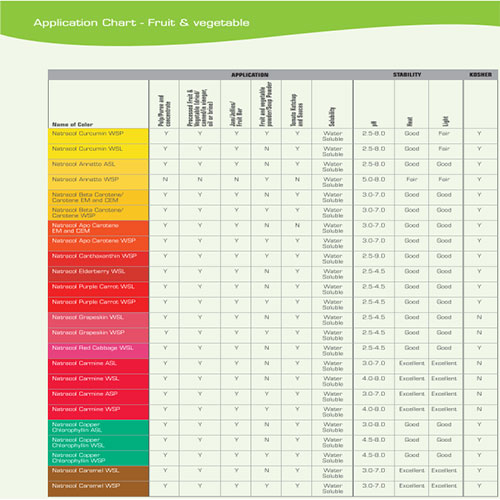
FOOD COLORING AND APPLICATION Color Order Chart
Bakery
Beverage
Confectionery
Pharmaceutical Products
Blended food colors
Dairy & Ice cream
Cosmetics & Toiletries
Soft Drink Concentrates
Squashes
Medicines
Seafood
All Edible preparations

Why food Colour?
If food does not taste good, people will not try it again. If it doesn’t look good, people may not try it at all. To understand why natural colors are so important for improving the visual appeal of food and beverage products, it is helpful to understand the science, psychology and history of colour.
The Science of Color
The science of color is sometimes referred to as chromatics, colorimetry or color science. It includes the perception of color by the human eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electromagnectic radiation in the visible range — commonly referred to as “light.” The color wheel can be divided into warm colors (those associated with the colors of the sun, such as red, yellow and orange) and cool colors (those associated with night, such as blue, purple and green). There are also three primary colors used to make all other colors: red, yellow, and blue. Secondary colors can be created by blending combinations of red, yellow or blue together to achieve orange, green or purple. This same color psychology phenomenon was also reported by the Journal of Consumer Research (March 2007), which found that consumer taste perceptions were directly influenced by beverage color. In fact, color was more influential in consumer product preference than price or even product quality — stunning evidence of just how important color is! In the March 2010 issue of Chemosensory Perception, it was reported that food color does indeed influence a food or drink’s taste and flavor perception in humans. “People’s judgments of flavor identity are often affected by the changing of a food or drink’s color (be it appropriate, inappropriate, or absent).”
Psychological Properties of Food Color
Red
Psychological Association: Physical
Positive: Physical courage, strength, warmth, energy, basic survival, ‘fight or flight’, stimulation, masculinity, excitement.
Negative: Defiance, aggression, visual impact, strain.
Blue
Psychological Association: Intellectual
Positive: Intelligence, communication, trust, efficiency, serenity, duty, logic, coolness, reflection, calm
Negative: Coldness, aloofness, lack of emotion, unfriendliness
Yellow
Psychological Association: Emotional
Positive: Optimism, confidence, self-esteem, extraversion, emotional strength, friendliness, creativity
Negative: Irrationality, fear, emotional fragility, depression, anxiety, suicide
Green
Psychological Association: Balance
Positive: Harmony, balance, refreshment, universal love, rest, restoration, reassurance, environmental awareness, equilibrium, peace
Negative: Boredom, stagnation, blandness, enervation
Violet (Purple)
Psychological Association: Spiritual
Positive: Spiritual awareness, containment, vision, luxury, authenticity, truth, quality.
Negative: Introversion, decadence, suppression, inferiority
Orange
Positive: Physical comfort, food, warmth, security, sensuality, passion, abundance, fun
Negative: Deprivation, frustration, frivolity, immaturity
Pink
Positive: Physical tranquility, nurture, warmth, femininity, love, sexuality, survival of the species
Negative: Inhibition, emotional claustrophobia, emasculation, physical weakness
Grey
Positive: Psychological neutrality
Negative: Lack of confidence, dampness, depression, hibernation, lack of energy
Black
Positive: Sophistication, glamour, security, emotional safety, efficiency, substance
Negative: Oppression, coldness, menace, heaviness
White
Positive: Hygiene, sterility, clarity, purity, cleanness, simplicity, sophistication, efficiency
Negative: Sterility, coldness, barriers, unfriendliness, elitism
Brown
Positive: Seriousness, warmth, Nature, earthiness, reliability, support
Negative: Lack of humour, heaviness, lack of sophistication
iron oxide red
iron oxide black
lutein
titanium dioxide
Description: also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2.
chlorophyllin copper complex potassium salts
Description: Chlorophyll is a natural green pigment which is obtained through extraction and refining processes from natural green plants or silkworm feces .
chlorophyllin copper complex sodium salts
tea green pigment
tea yellow pigment
erythrosine, erythrosine aluminum lake
indigotine,indigotine aluminum lake
orange yellow
riboflavin
black bean red
black currant red
red rice red
monascus red
red kojic red
Description: Widely adopted to color ready-to-serve meat and sausages (e.g. brined pig feet, chichen wings, drumsticks, chicken feet), pickled meat, instant noodles, condiments, puffed food, wines, jelly, pastry, confectionary and fillings of baked food etc.
peanut skin red
turmeric
monascus red
red kojic red
Description: Widely adopted to color ready-to-serve meat and sausages (e.g. brined pig feet, chichen wings, drumsticks, chicken feet), pickled meat, instant noodles, condiments, puffed food, wines, jelly, pastry, confectionary and fillings of baked food etc.
peanut skin red
turmeric
curcumin
caramel colour
Description: It is made by heat treatment of carbohydrates, in general in the presence of acids, alkalis, or salts, in a process called caramelization.
rose laevigata michx brown
cocoa husk pigment
Description: used in soft drinks, liqueur, carbonated beverages, candy, pastries color equipment, soy milk beverages, ice cream, cookies and other coloring
quinoline yellow
brillant blue,brilliant blue aluminum lake
radish red
basella rubra red
roselle red
tartrazine tartrazine aluminum lake
grape skin extract
sunset yellow,sunset yellow aluminum lake
mulberry red
hippophae rhamnoides yellow
carmoisine(azorubine)
jujube pigment
natural amaranthus red
allura red
carmine cochineal
annatto extract
ponceau 4R,ponceau 4R aluminum lake
Description: sometimes called roucou or achiote, is derived from the seeds of the achiote trees of tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The seeds are sourced to produce a carotenoid-based yellow to orange food coloring and flavour.
corn yellow
cowberry red
spirulina blue(algae blue,lina blue)
gardenia yellow
gardenia blue
vegetable carbon(carbon black)
gromwell red
lac dye red(lac red)
beet red
natural carotene
lycopene






Food Colors - Origins and Chemistry
Food colours are divided into 3 main types:
Natural, Nature Identical and Synthetic
Natural Colours
Natural Food Colours are dyes or pigments extracted from natural sources like vegetables, plants and insects. If extracted with care, these Colours can provide versatile colouring application with safe usage in different types of Food Products. Since last 25 years, Tanya has been manufacturing Natural Food Colours made strictly from plants and vegetables which serve the needs of a variety of Food and Beverage Industries. These colours are used to give visual appeal and colour uniformity & consistency to Food and Beverages.These are obtained from natural sources such as grasses, leafy vegetables, fruit skins, roots and seeds of plants. Animals can also be a source of food colourings. Cochineal, or carminic acid, is a red colour that is obtained from the bodies of certain scale insects. These feed off cactus leaves and their bodies are commercially harvested in Africa, Spain and Central America. Their bodies are dried and crushed to extract the red coloring.
Nature Indentical Colours
Obtaining colors from natural sources can be costly and their quality can vary. To overcome this, chemists have found ways to make identical colors in the laboratory. This improves their purity and may also cost less Nature identical colors are exactly the same molecules found in natural sources but they are made synthetically. The main chemical classes are: flavonoids, found in many flowers, fruits and vegetables indigoid, found in beetroot carotenoids, found in carrots, tomatoes, oranges and most plants. Carrots contain an orange molecule called beta-carotene which is part of this group. Most natural and nature identical colors can dissolve in oil but do not dissolve in water. This means it is difficult to add them directly to foods. They are usually processed to form their sodium or potassium salt. This makes them soluble in water and suitable for use in foods. They may also be dissolved in oil and incorporated into water-soluble beadlets.
Synthetic Colors